The AI industry is facing a growing agency gap. While startups rapidly build autonomous agents in Python, large enterprises rooted in Java ecosystems are struggling to keep pace. The quick-fix LLM wrappers of 2024 promised easy AI integration, but they fail where it matters most: state management, orchestration, reliability, and real business logic. In short, they don’t scale to enterprise reality. This is where the Spring AI Alibaba Framework enters the picture.
In this blog, we explore the shift from simple chatbots to agentic workflows systems where AI plans, coordinates, and acts. We’ll see how Spring AI Alibaba brings this evolution to Java, offering enterprises the structure, governance, and stability needed for production-grade AI.
Inside The Rise Of Multi-Agent AI Systems
The move from a chatbot to an AI agent is more than a technical improvement it’s a shift in how AI actually works. Traditional chatbots follow a simple question-and-answer loop. You ask something, get a reply, and the interaction ends. This breaks down when tasks require planning, multiple steps, or coordination to achieve a real outcome.
A Multi-Agent System (MAS) changes this model. It acts like a team of digital workers, each with a defined role research, validation, or execution working toward a shared goal. This is where Spring AI Alibaba shines. Its graph-based runtime enables agents to collaborate intelligently, execute full workflows, and deliver reliable, outcome-driven AI for enterprise needs.
The Challenges Java Developers Faced Before Spring AI Alibaba
Before Spring AI Alibaba emerged, Java teams faced major hurdles adopting AI in production. Most modern AI frameworks were built for Python, creating a Python Monopoly Gap for enterprises running on Java in banking, retail, and logistics. Rewriting stable, business-critical systems just to add AI was impractical and risky.
Teams also struggled with the Statelessness Trap and an Integration Void. LLMs don’t retain memory by default, forcing developers to build complex context management. Integrating with enterprise tools like Nacos required fragile, manual setups. Together, these barriers made AI adoption slow, expensive, and unreliable.
The Solution provided By The Spring AI
Spring AI Alibaba acts as an operating system for AI agents in the Java ecosystem, bringing true agentic intelligence directly into the JVM. Instead of forcing enterprises to rely on Python-based frameworks and fragile bridge services, it enables Java teams to build advanced, stateful agent systems using familiar tools like Spring Boot, Maven, and Gradle. This shift finally removes the dependency gap and makes enterprise-grade agent orchestration a first-class citizen in Java.
At the heart of the framework is Spring AI Alibaba Graph, a stateful orchestration engine built for real world workflows. It remembers context, intermediate decisions, and paused states allowing agents to wait for databases or external services and resume seamlessly. Combined with deep integration into enterprise middleware like Nacos for agent-to-agent communication, Sentinel for cost and flow control, and built-in observability, Spring AI Alibaba delivers AI systems that are not just intelligent, but controlled, auditable, and ready for production at scale.
Spring AI Alibaba: Enterprise-Grade Agentic System Architecture
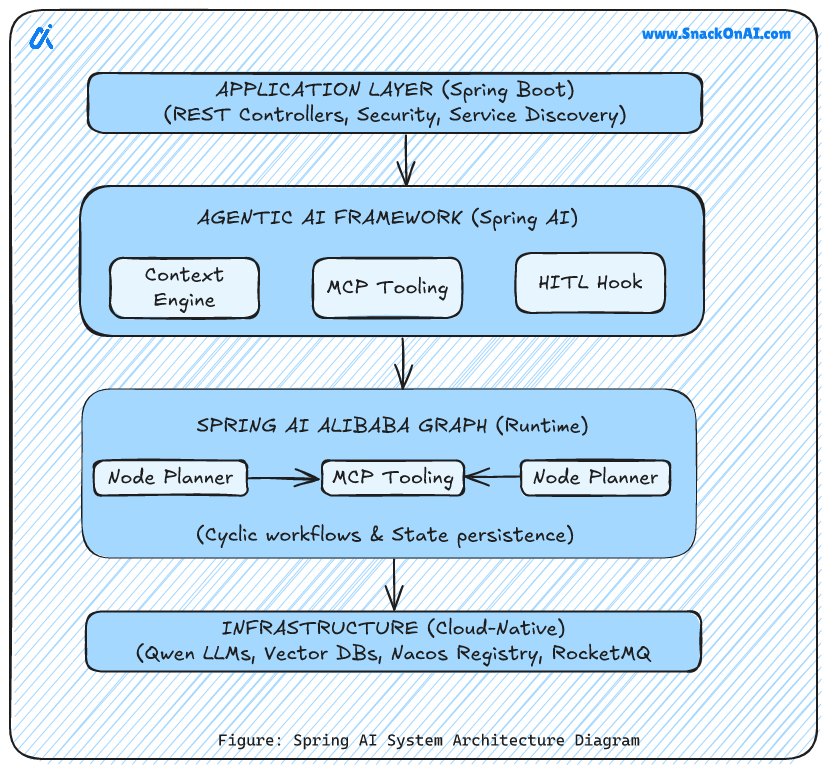
This architecture illustrates how Spring AI Alibaba enables scalable, production-ready agentic workflows within a modern Java ecosystem.
Application Layer (Spring Boot):
Exposes REST APIs and handles security, service discovery, and user requests.Agentic AI Framework (Spring AI):
Provides a Context Engine for memory, MCP Tooling for tool calls, and HITL hooks for human-in-the-loop control.Spring AI Alibaba Graph (Runtime):
Orchestrates workflows using node planners, supports cyclic flows, and persists state.Infrastructure Layer (Cloud-Native):
Supplies LLMs (Qwen), vector databases, service registry (Nacos), and messaging (RocketMQ).
Together, these layers enable scalable, observable, and enterprise-ready AI agents.
Challenges & Considerations To Keep In Mind
Multi-agent systems offer powerful capabilities, but they also bring important engineering trade-offs that teams must address early. One major balance is latency versus accuracy. Adding more agents increases reasoning depth, but it also slows response time. For many use cases, a single well-tuned LLM is enough, while complex or high-stakes tasks justify multiple specialized agents working together.
Cost and control are equally critical. Cyclic workflows can create infinite loops without proper safeguards, making flow-control tools like Sentinel essential for budget and stability. Observability also becomes harder, requiring deep tracing and structured logs to understand agent decisions. Designing for visibility isn’t optional it’s foundational for safe production use.
Real-World Use Cases: Where Spring AI Alibaba Delivers Real Value
Spring AI Alibaba demonstrates its value in real enterprise scenarios where reliability and governance matter. In customer support, coordinated agents can classify tickets, retrieve accurate knowledge-base responses, and escalate only critical cases to humans. In financial services, agents work together to validate transactions, perform compliance checks, and generate audit-ready reports, enabling faster yet controlled decision-making.
In e-commerce and logistics, agents can coordinate inventory, pricing, and demand forecasting to optimize supply chains in real time. For enterprise analytics, they can query data warehouses, run reasoning workflows, and deliver executive-ready insights. These are not experimental bots they are production-grade, scalable, and deeply integrated into Spring-based systems.
References & Further Reading
Here are a few essential resources to help you explore the theory and practice behind agentic AI and Spring AI Alibaba. Together, they cover how agents reason before acting, how complex tasks are decomposed into multiple agents, and how long-term memory and autonomy are designed in modern AI systems.
Spring AI Alibaba bridges the agency gap by bringing scalable, governed, and production-ready multi-agent intelligence to the Java enterprise ecosystem.
